
We can therefore predict the CH 3–N portion of the molecule to be roughly tetrahedral, similar to methane: The four bonds around carbon mean that it must be surrounded by four bonding electron pairs in a configuration similar to AX 4. We can treat methyl isocyanate as linked AX mE n fragments beginning with the carbon atom at the left, which is connected to three H atoms and one N atom by single bonds. In addition, there was significant damage to livestock and crops.
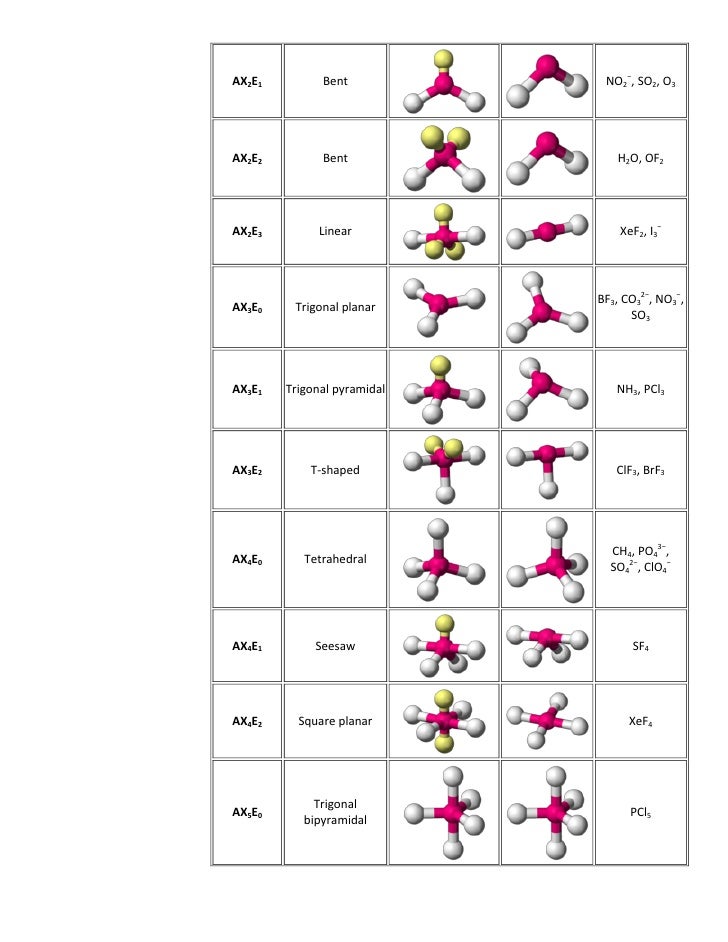
The resulting highly exothermic reaction caused a rapid increase in pressure that ruptured the tanks, releasing large amounts of methyl isocyanate that killed approximately 3800 people and wholly or partially disabled about 50,000 others. In 1984, large quantities of Sevin were accidentally released in Bhopal, India, when water leaked into storage tanks. We will demonstrate with methyl isocyanate (CH 3–N=C=O), a volatile and highly toxic molecule that is used to produce the pesticide Sevin. The VSEPR model can be used to predict the structure of somewhat more complex molecules with no single central atom by treating them as linked AX mE n fragments. In our discussion we will refer to Figure 5.1.2 and Figure 5.1.3, which summarize the common molecular geometries and idealized bond angles of molecules and ions with two to six electron groups. We will illustrate the use of this procedure with several examples, beginning with atoms with two electron groups. Assign an AX mE n designation then identify the LP–LP, LP–BP, or BP–BP interactions and predict deviations from ideal bond angles.Determine the electron group arrangement around the central atom that minimizes repulsions.Draw the Lewis electron structure of the molecule or polyatomic ion.Using this information, we can describe the molecular geometry The arrangement of the bonded atoms in a molecule or a polyatomic ion in space., the arrangement of the bonded atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion.
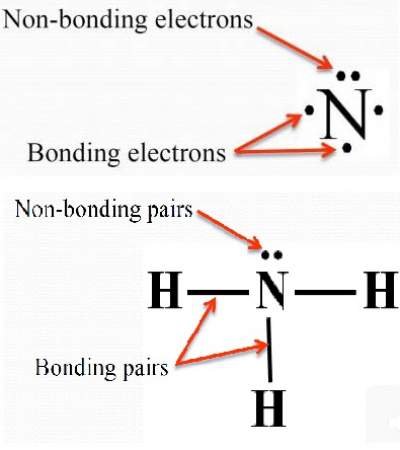
From the BP and LP interactions we can predict both the relative positions of the atoms and the angles between the bonds, called the bond angles The angle between bonds. Each group around the central atom is designated as a bonding pair (BP) or lone (nonbonding) pair (LP).
In the VSEPR model, the molecule or polyatomic ion is given an AX mE n designation, where A is the central atom, X is a bonded atom, E is a nonbonding valence electron group (usually a lone pair of electrons), and m and n are integers. That is, the one that minimizes repulsions. \)įigure 5.1.2 Geometries for Species with Two to Six Electron Groupsįigure 5.1.1 Common Structures for Molecules and Polyatomic Ions That Consist of a Central Atom Bonded to Two or Three Other Atoms Groups are placed around the central atom in a way that produces a molecular structure with the lowest energy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
